Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Suzuki, Hiroshi; Kusunoki, Koichi*; Hatanaka, Yuichi*; Mukai, Tomohisa*; Tasai, Akira*; Kanematsu, Manabu*; Kabayama, Kenji*; Harjo, S.
Measurement Science and Technology, 25(2), p.025602_1 - 025602_8, 2014/02
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:58.71(Engineering, Multidisciplinary)In the modern society, architectural and civil engineering structures such as reinforced concrete buildings require high seismic performance to minimize the "megarisk" exposed from urban earthquake hazards. In the reinforced concrete structures, the bond resistance between rebar and concrete is one important parameter for discussing its performance and it has been typically evaluated by measuring the strain distribution along the embedded rebar. Here we present an in-situ strain and stress measurements for the rebar in the reinforced concrete using time-of-flight neutron diffraction as a novel alternative technique to typical strain gauges. It was demonstrated in this study that the three-dimensional deformation behavior of the embedded rebar in normal-strength concrete, cured in air, can be accurately measured under pull-out loading using time-of-flight neutron diffraction.
Tsuchiya, Yoshinori*; Suzuki, Hiroshi; Umeno, Takahiro*; Machiya, Shutaro*; Osamura, Kozo*
Measurement Science and Technology, 21(2), p.025904_1 - 025904_4, 2010/01
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:73.38(Engineering, Multidisciplinary)Strain measurements under loading at cryogenic temperatures are much requested for investigation of the stress/strain effect on the critical current for composite superconductors. In order to provide in-situ measurements of the lattice strain, a cryogenic load frame with a GM refrigerator has been developed, which is suitable for the neutron diffraction facility RESA equipped at JRR-3 in JAEA. The lowest temperature of 4.8 K was achieved, while the capacity of the load frame was 10 kN. Using the present cryogenic load frame, plane spacing measurement was performed under loading for two specified samples of 316 stainless steel and engineering YBCO coated conductor. The relation between applied stress/strain and lattice strain has been made clear in a wide range of temperatures.
 -ray and 14 MeV neutron irradiation
-ray and 14 MeV neutron irradiationTo, Kentaro*; Shikama, Tatsuo*; Nagata, Shinji*; Tsuchiya, Bun*; Yamauchi, Michinori; Nishitani, Takeo
Measurement Science and Technology, 17(5), p.955 - 959, 2006/05
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:43.68(Engineering, Multidisciplinary)The effect of photobleaching on radiation-induced transmission loss of fused-silica-core optical fibres was examined under  Co
Co  -ray and 14 MeV neutron irradiation. In the visible wavelength range, the radiation-induced transmission loss could be reduced by photobleaching under both types of irradiation. It is considered that the number of radiation-induced defects such as E' centre and NBOHC that cause optical absorption was reduced by photobleaching. For using optical fibres in the visible wavelength range as light guides or image guides, photobleaching is an effective technique to improve their radiation resistance. However, a so-called microbending loss is induced by radiation in the entire wavelength range. The loss response to photobleaching was different under
-ray and 14 MeV neutron irradiation. In the visible wavelength range, the radiation-induced transmission loss could be reduced by photobleaching under both types of irradiation. It is considered that the number of radiation-induced defects such as E' centre and NBOHC that cause optical absorption was reduced by photobleaching. For using optical fibres in the visible wavelength range as light guides or image guides, photobleaching is an effective technique to improve their radiation resistance. However, a so-called microbending loss is induced by radiation in the entire wavelength range. The loss response to photobleaching was different under  -ray and fast-neutron irradiation. The loss under the
-ray and fast-neutron irradiation. The loss under the  -ray irradiation increased due to photobleaching, while that under the fast-neutron irradiation decreased. It is considered that there are multiple reasons for the radiation-enhanced microbending loss. In general, it is concluded that the photobleaching technique is effective in improving the radiation resistance of fused-silica-core optical fibres under neutron and moderate flux radiation environments.
-ray irradiation increased due to photobleaching, while that under the fast-neutron irradiation decreased. It is considered that there are multiple reasons for the radiation-enhanced microbending loss. In general, it is concluded that the photobleaching technique is effective in improving the radiation resistance of fused-silica-core optical fibres under neutron and moderate flux radiation environments.
Murai, Yuichi*; Oiwa, Hiroshi; Sasaki, Toshio*; Kondo, Masahiko; Yoshikawa, Shinji; Yamamoto, Fujio*
Measurement Science and Technology, 16(7), p.1459 - 1468, 2005/07
Times Cited Count:31 Percentile:81.42(Engineering, Multidisciplinary)Air-water two-phase flow in a helically coiled tube is investigated using backlight imaging tomography to elucidate the effect of centrifugal acceleration on phase distribution and interfacial structure. Superficial velocities up to 6m/s in 20mm-diameter tube are tested. We focused on a slug flow regime in which centrifugal acceleration dominates the flow. The interfacial structure is visualized in six directions using a set of originally designed mirror-mounted water jackets. A temporal expansion image is made from line-sampled images, and is used to reconstruct phase distribution through a linear backward projection algorithm. The present topography measurement showed various new features of gas-liquid two-phase flow in a helically coiled tube, such as a wall-covering effect in the case of high superficial velocity.
Higuchi, Kensuke*; Kimura, Kakuryo*; Mizuno, Akitoshi*; Watanabe, Masahito*; Katayama, Yoshinori; Kuribayashi, Kazuhiko*
Measurement Science and Technology, 16(2), p.381 - 385, 2005/02
Times Cited Count:43 Percentile:87.11(Engineering, Multidisciplinary)X-ray diffraction and density measurements have been simultaneously performed to investigate the atomic structure of molten silicon in wide temperature range including undercooling region by using the electromagnetic levitation technique. The density was obtained from the mass and the shape of levitated sample by non-contact method based on the image analysis technique. X-ray diffraction experiments were performed by using the synchrotron radiation at SPring8, Japan. From structural analysis of undercooled molten silicon, first nearest neighbour coordination numbers and interatomic distances were about 5 and 2.48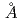 with no dependence on temperature in the range of 1900-1550 K. We conclude as a result that the short-range order based on tetrahedral bonds of undercooled molten silicon does not change with the degree of undercoolings but medium-range order changes by the degree of undercoolings.
with no dependence on temperature in the range of 1900-1550 K. We conclude as a result that the short-range order based on tetrahedral bonds of undercooled molten silicon does not change with the degree of undercoolings but medium-range order changes by the degree of undercoolings.